Kia Picanto (JA): Intake And Exhaust System / Turbo Manifold Module
Components and components location
| Components |
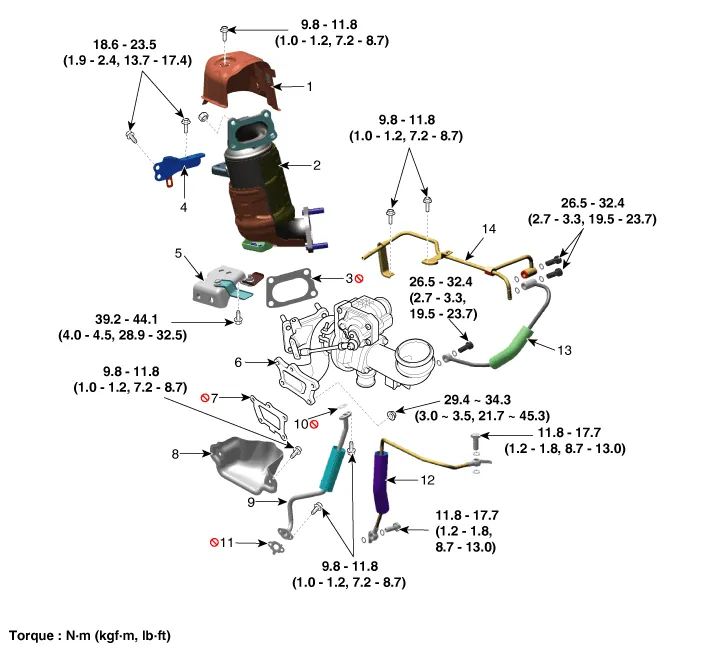
| 1. Coupler heat protector 2. Warm-up catalytic converter (WCC) 3. Warm-up catalytic converter (WCC) gasket 4. Warm-up catalytic converter (WCC) upper stay 5. Exhaust manifold upper stay 6. Turbocharger manifold 7. Turbocharger manifold gasket | 8. Exhaust manifold heat protector 9. Oil drain pipe & hose 10. Oil drain pipe gasket A 11. Oil drain pipe gasket B 12. Oil feed pipe & hose 13. Water feed pipe & hose 14. Water drain pipe & hose |
| Components |
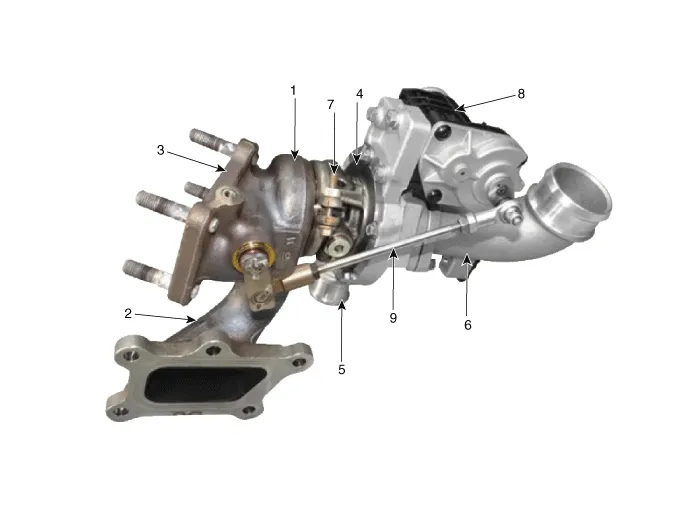
| 1. Turbine housing 2. Turbine inlet 3. Turbine outlet 4. Compressor housing 5. Compressor outlet | 6. Compressor inlet 7. Center housing 8. EWGA (Electric Waste Gate Actuator) 9. Actuator rod |
Repair procedures
| Removal and Installation |
| 1. | Remove the engine room under cover.
(Refer to Engine and Transaxle Assembly - "Engine Room Under Cover")
|
| 2. | Drain the engine coolant.
(Refer to Cooling System - "Coolant")
|
| 3. | Remove the air cleaner assembly.
(Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Air Cleaner")
|
| 4. | Remove the front muffler.
(Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Muffler")
|
| 5. | Disconnect the electric waste gate actuator (EWGA) extension connector (A).
|
| 6. | Remove the front oxygen sensor.
(Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)")
|
| 7. | Disconnect the water hose (A).
|
| 8. | Disconnect the turbo charger water drain pipe hose (A).
|
| 9. | Remove the coupler heat protector (A) and water drain pipe (B)
|
| 10. | Remove the exhaust manifold stay (A).
|
| 11. | Remove the warm-up catalytic converter (WCC) upper stay (A) and then remove the warm-up catalytic converter (WCC) (B).
|
| 12. | Remove the water feed hose & pipe (A) and oil drain pipe (B).
|
| 13. | Remove the oil feed pipe (A).
|
| 14. | Remove the exhaust manifold heat protector (A).
|
| 15. | Remove the turbo manifold module (A) with the gasket.
|
| 16. | Install in the reverse order of removal. |
| On-vehicle Inspection |
| Turbocharger Diagnostic Flow |
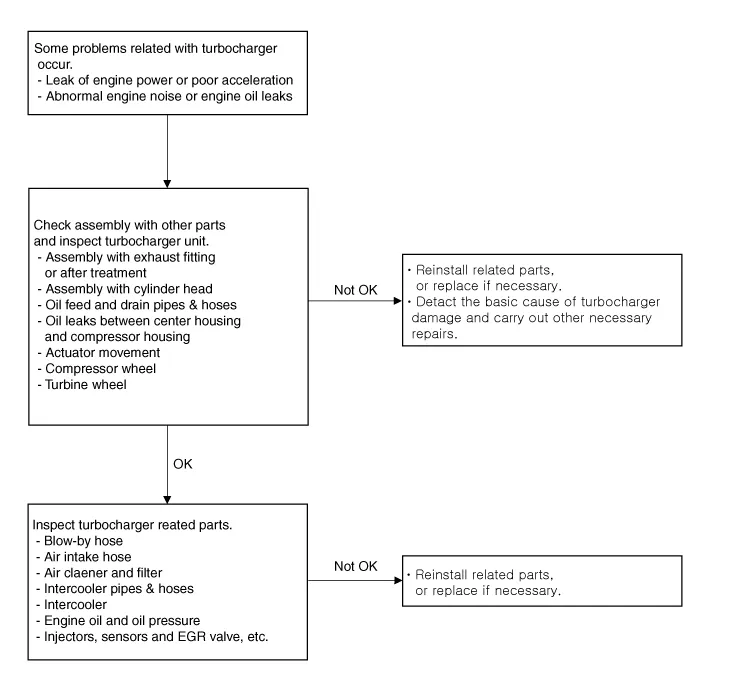
| 1. | Check the assembly of the turbocharger and the exhaust fitting (or the after treatment).
Gas leakage caused by lack of gasket or inadequately tightened mounting bolts (or nuts) may cause abnormal engine noise. If
the cause of the problem is detected, retighten the mounting bolts (or
nuts) to the specified torque or replace the gasket or damaged parts
with new ones if necessary. |
| 2. | Check the assembly of the exhaust manifold and the cylinder head.
Gas leakage caused by lack of gasket or inadequately tightened mounting bolts (or nuts) may cause abnormal engine noise. If
the cause of the problem is detected, retighten the mounting bolts (or
nuts) to the specified torque or install a new gasket if necessary. |
| 3. | Check the turbocharger oil feed pipe & hose and oil drain pipe & hose.
If a gas leak occur as a gasket was not installed or mounting bolts were tightened inadequately, it may cause oil leaks. If
the oil feed pipe & hose is damaged, engine oil is not supplied
sufficiently to the turbocharger then it may damage the turbocharger. If
the oil drain pipe & hose is damaged and clogged, engine oil is not
drained smoothly then it may cause oil leaks from the turbocharger. If
the cause of the problem is detected, retighten the mounting bolts (or
nuts) to the specified torque or replace the gasket or damaged parts
with new ones if necessary. |
| 4. | Check for oil leakage between center housing and compressor housing.
Damaged O-ring (gasket) between the center housing and the compressor housing may cause oil leakage. If an oil leak is detected, replace the turbocharger with a new one. |
| 5. | Check the turbocharger actuator.
Damaged turbocharger actuator may cause lack of engine power and poor acceleration. If the actuator rod does not move, replace the turbocharger with a new one. |
| 6. | Check the turbocharger compressor wheel.
Damaged compressor wheel may cause abnormal noise from the turbocharger and poor acceleration. If the compressor wheel are damaged or deformed, replace the turbocharger with a new one. |
| 7. | Check the turbocharger turbine wheel.
Damaged turbine wheel may cause abnormal noise from the turbocharger and poor acceleration. If the turbine wheel are damaged or deformed, replace the turbocharger with a new one. |
| 1. | Check the blow-by hose. (Refer to FL group)
If
the breather hose is bent or clogged, the internal pressure in the
engine will increase and engine oil will not be supplied smoothly to the
turbocharger, causing damage to the turbocharger and oil leakage. If the cause of the problem is detected, replace the breather hose or the related parts with new ones. |
| 2. | Check the air intake hose connected to the turbocharger.
If
the cross-section of the hose diminishes as the air intake hose is bent
or crushed, intake air to the turbocharger will be reduced and the
pressure in front of turbocharger will drop, causing damage to the
turbocharger or oil leakage. If the air intake hose is detached or torn,
foreign substances may go into the turbocharger causing damage to it. If the air intake hose is damaged, replace it with a new one. |
| 3. | Check the air cleaner.
If
the air cleaner filter is moistened or polluted excessively or a
non-genuine part is used, intake air to the turbocharger will be reduced
and the pressure in front of turbocharger will drop, causing damage to
the turbocharger and oil leakage. If the air cleaner filter is moistened or polluted excessively, replace it with a new one.
|
| 4. | Check the intercooler hoses & pipes.
If
the intercooler hoses & pipes are damaged or disconnected, oil
leakage may occur from the hoses & pipes and the turbocharger may
exceed the permissible speed causing damage to the turbocharger. If the intercooler hoses & pipes are damaged, replace them with new ones.
|
| 5. | Check the intercooler.
If the intercooler is damaged, the turbocharger may exceed the permissible speed causing damage to the turbocharger. If the intercooler is damaged, replace them with a new one.
|
| 6. | Check the engine oil.
If
the engine oil level is low, amount of engine oil fed to turbocharger
will be reduced causing the bearings in the turbocharger to adhere due
to insufficient lubrication and cooling. If the cause of the problem is detected, add or change engine oil.
|
| 7. | Check the engine oil pressure.
If
the engine oil level is low, amount of engine oil fed to turbocharger
will be reduced causing the bearings in the turbocharger to adhere due
to insufficient lubrication and cooling. If the cause of the
problem is detected, add or change engine oil. If foreign substances are
accumulated on the oil screen, wash the oil screen and replace the
injector’s washer with a new one after checking the injectors for gas
leaks. Check the engine oil-related parts, such as oil pump, if
necessary.
|
| 8. | Check the injectors, sensors, etc. (Refer to FL group)
Improper operation of the injectors, sensors, EGR valve, etc. may cause diminished engine power. If the cause of the problem is detected, replace the related parts with new ones. |
Components and components location Components 1. Manifold absolute pressure sensor (MAPS) 2. Intake manifold 3. Electronic throttle body control (ETC) module gasket 4.
Components and components location Components 1. Intercooler air guard 2. Intercooler 3. Recirculation valve (RCV) control solenoid valve & vacuum hose 4.
Other information:
Kia Picanto (JA) 2017-2025 Service & Repair Manual: Headlamp Leveling Switch
Schematic diagrams Circuit Diagram Repair procedures Removal 1.Disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal. 2.Remove the crash pad lower panel. (Refer to Body - "Crash Pad Lower Panel") 3.Remove the crash pad side switch (A) after loosening the mounting screws.
Kia Picanto (JA) 2017-2025 Service & Repair Manual: Horn
Components and components location Component Location 1. Horn switch 2. Horn relay 3. Horn 4. Clock spring Repair procedures Removal 1.Disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal. 2.Remove the engine room under cover. G 1.
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Kia Picanto Owners Manual
- Kia Picanto Service Manual
- Engine Electrical System
- Engine Mechanical System
- Windshield Wiper/Washer
- New on site
- Most important about car















